The Nervous system has three major functions:
1. Sensory – monitors and responds to internal & external stimuli to maintain homeostasis.
2. Motor – control movement
3. Regulation - regulates bodily functions
The Brain Videos...Watche them all!
3. Regulation - regulates bodily functions
The Brain Videos...Watche them all!
The Organs of the Nervous system1. brain
2. spinal cord
3. nerves
4. sensory organs - the eyes, ears, nose, tongue and sensory receptors in skin,
4. sensory organs - the eyes, ears, nose, tongue and sensory receptors in skin,
joints,
muscles and other parts of the body.
There
Video on Neurons
Bill Nye on the Brain
3 types of Neurons

Motor neurons communicate to move muscles
Sensory neurons communicate with your senses
Interneurons are nerve cells found entirely within the central nervous system that acts as a link between sensory neurons and motor neurons.
Bill Nye on the Brain
3 types of Neurons

Motor neurons communicate to move muscles
Sensory neurons communicate with your senses
Interneurons are nerve cells found entirely within the central nervous system that acts as a link between sensory neurons and motor neurons.
How does the nervous system interact with other body systems? Click here!
The human
nervous system consists of billions of nerve
cells (or neurons) plus supporting (neuroglial) cells. Neurons are able to
respond to stimuli (such as touch, sound, light, and so on), conduct impulses,
and communicate with each other (and with other types of cells like muscle
cells).
Parts of a Neuron
Soma - the cell body
The Nucleus of a neuron is located in the cell body.
Dendrites extend out from the cell body and receive messages from the axon terminal during a synapse.
Axons extend out from the cell body and send messages during a synapse.
The Nucleus of a neuron is located in the cell body.
Dendrites extend out from the cell body and receive messages from the axon terminal during a synapse.
Axons extend out from the cell body and send messages during a synapse.
Myelin sheath surrounds the axon and helps move impulses faster.
Impulses typically travel along neurons at a speed of anywhere from 1 to 120 meters per second!
The axon of one neuron doesn't touch the dendrites of the next. Nerve signals
have to move across a tiny gap, the Synaptic Gap. To get across the gap they have to change from
electrical signals into chemical signals then back into electrical signals.
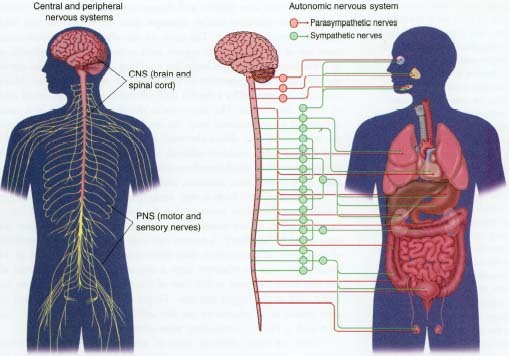
The Nervous System is divided into 2 parts.
Click here for the Powerpoint
Click here for the Powerpoint
The central nervous system (CNS) spinal cord
brain
Its main job is to get the information from the body and send out instructions.
brain
Its main job is to get the information from the body and send out instructions.
The peripheral nervous system (PNS)
nerve tissue outside the brain
sensory organs
This system sends the messages from the brain to the rest of the body.
nerve tissue outside the brain
sensory organs
This system sends the messages from the brain to the rest of the body.
The peripheral nervous system is divided into two major parts:
somatic nervous system - controls voluntary functions, movement, controls the skeletal
muscles
autonomic nervous system - controls involuntary functions, controls cardiac and smooth
muscles, and glands.
The autonomic nervous system is divided into two major parts:
the sympathetic system- fight or flight, stimulatory stress responses.
the parasympathetic system - rest and digest, salavation, digestion, dilation
somatic nervous system - controls voluntary functions, movement, controls the skeletal
muscles
autonomic nervous system - controls involuntary functions, controls cardiac and smooth
muscles, and glands.
The autonomic nervous system is divided into two major parts:
the sympathetic system- fight or flight, stimulatory stress responses.
the parasympathetic system - rest and digest, salavation, digestion, dilation
Glands...what glands? The Endocrine System!
The endocrine system is the system of glands, each of which secretes different types of hormones directly into the bloodstream to regulate the body.
Hormones
What is a hormone? It is a chemical that
has a high level of specificity, which means that it will only react with a
specific receptor site in your body. The lock and key analogy is often used to
explain this specificity, and it is a great way to think about how hormones
work. Hormones convey important information to the body, including such
instructions as cell division and growth, appetite suppression, acid secretion,
calcium absorption, and red and white blood cell production. Hormones are
secreted by endocrine glands. There are eight major endocrine glands. Those
glands, along with their main functions, are listed below:
Pituitary gland -
regulates other endocrine glands; secretes growth hormone.
Thyroid - regulates metabolic
rate.Thymus - assists in development of immune system.
Adrenal gland - regulates fluid and sodium balance; emergency warning system under stress.
Ovary - controls development of secondary sex characteristics and functioning of sex organs.
Testis - controls development of secondary sex characteristics and functioning of sex organs.
Pancreatic islets - helps regulate blood sugar.
Pineal gland - believed to regulate biorhythms and moods and stimulate the onset of puberty.
Fight or Flight ResponsesWhen our senses perceive an environmental stress such as danger or a threat, cells in the nervous and endocrine systems work closely together to prepare the body for action. Often referred to as the fight or flight or stress response, this remarkable example of cell communication elicits instantaneous and simultaneous responses throughout the body.

Your Senses can fool you...Check out these cool illusions Auditory Illusions Optical Illusions 1 Optical Illusions 2 Optical Illusions 3
Optical Illusions 4
Can you say the color name not read the word?

Your Brain processes words and reading first, thats what makes this tsak so difficult...
That's all for now....
Can you say the color name not read the word?

Your Brain processes words and reading first, thats what makes this tsak so difficult...
That's all for now....
Mrs. Sandoval
0 comments:
Post a Comment