The atmosphere can do some amazing things. This tornado, started by a thunderstorm, might last only a minute or two before its winds die down. Or it might last for hours. Knowing about the different types of severe weather can help you know how to stay safe.
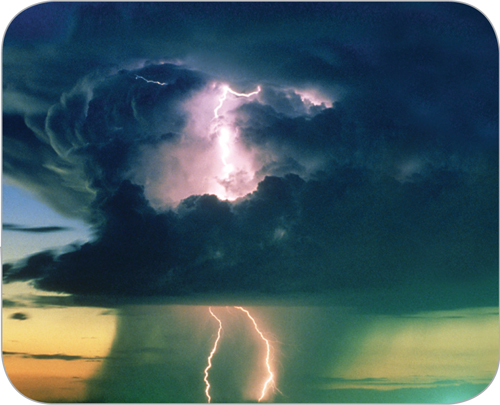
If you’ve ever watched clouds, you know they constantly change. A cumulus cloud that becomes massive and tall is a towering, dark cumulonimbus cloud (kyew myuh loh NIHM bus)—the type of cloud that can form thunderstorms. A thunderstorm is a weather event that includes rain, strong winds, thunder, and lightning. The average thunderstorm is 25 km across and lasts only 30 min. However, some thunderstorms are huge and long-lasting, especially those that happen in the central part of the United States.
Thunderstorm Formation
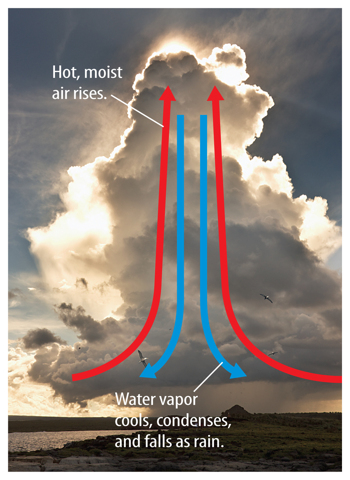
When warm, moist air rises, it cools. Some of the cooled air sinks, starting the process of convection. Thunderstorms usually have many convection flows of air moving up and down. As the air cools, some of the water vapor in the air condenses and clouds form. As shown in Figure 1, a huge cloud can grow as more warm, moist air rises and more water vapor condenses. When the water droplets become large enough, rain starts to fall. The largest thunderstorms form where a warm, moist air mass meets a cool, dry air mass.
1. Key Concept Check How do thunderstorms form?
Figure 1 Cool air sinks and warm air rises, creating convection flow within clouds. This cumulonimbus cloud likely will form a thunderstorm.
Thunder and Lightning
You probably have heard thunder rumble and seen lightning flash across the sky. But do you know what causes them? Lightning is electricity discharged within a cloud, between clouds, or between a cloud and the ground. When a bolt of lightning rapidly heats air molecules, it produces a loud bang—thunder. Thunder happens at the same time as lightning. However, because light travels faster than sound, you often see a flash of light before you hear a rumble of thunder.
What causes lightning? Convection causes molecules to bump into each other, creating tiny electric charges. As illustrated in Figure 2, negative charges build up in some areas of a cloud and are attracted to positive charges. Lightning strikes when negatively and positively charged areas connect. Positive charges on Earth will flow to a high point and get close to negative charges in the sky. That’s why lightning usually strikes mountaintops, tall trees, and buildings.
2.  Reading Check How does lightning form?
Reading Check How does lightning form?
 Reading Check How does lightning form?
Reading Check How does lightning form?
Figure 2 Lightning strikes when negative charges within a cloud connect with positive charges on Earth’s surface, in another area of the cloud, or in another cloud.
Thunderstorm Impacts
Although thunderstorms bring much-needed rain to many areas, they also can be dangerous. Lightning strikes can be deadly and sometimes start wildfires. Thunderstorms that drop rain quickly can cause flash flooding. Hail also is a danger to people, wildlife, and property. And the strong winds associated with thunderstorms can knock over trees and power lines.
Forecasting Weather forecasters monitor thunderstorms with weather satellites and use radar to track a storm’s precipitation and winds, as shown in Figure 3. They use computer models to predict whether a thunderstorm is likely. A model combines recent weather data with hundreds of calculations.
Safety When weather models indicate a thunderstorm is likely, forecasters issue a thunderstorm watch. When there is a thunderstorm, they issue a thunderstorm warning. If a thunderstorm warning is issued for your area, go inside to stay safe.
Figure 3 Weather forecasters use computer models to predict thunderstorms and other weather events.
Tornadoes
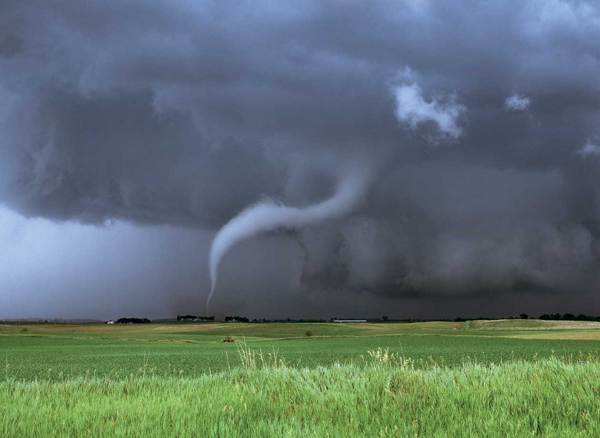
A violent, whirling column of air in contact with the ground is a tornado, or a twister. Sometimes tornados are so powerful they can destroy everything in their paths. Tornadoes usually do not last long—sometimes just a few seconds—but some can last much longer.
Tornado Formation
Tornadoes can form during thunderstorms and hurricanes. Within a thunderstorm, air warmed at Earth’s surface rises quickly. Sometimes rising air can rotate and form a funnel in the clouds. The spinning funnel grows downward and sometimes reaches Earth’s surface.
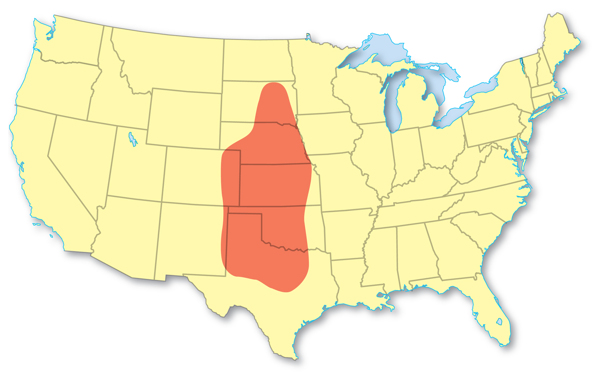
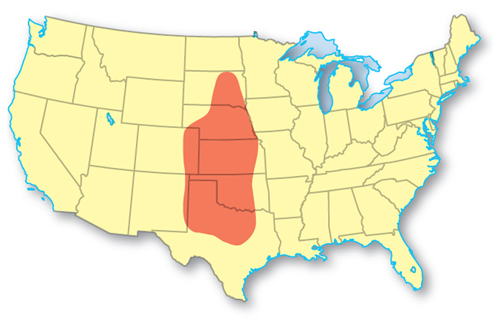
Over 1,000 tornadoes occur each year in the United States. Tornadoes occur in all 50 states but are most common in the area called Tornado Alley, shown in Figure 4. The huge thunderstorms that happen in this area cause the tornadoes.
1. Key Concept Check How are tornadoes related to thunderstorms and hurricanes?
Figure 4 The United States has more tornadoes than anywhere else on Earth. Most of them occur in the highlighted area called Tornado Alley.
 Visual Check Which states are part of Tornado Alley?
Visual Check Which states are part of Tornado Alley?
Tornado Impacts
When a tornado touches down, it pulls objects on Earth’s surface up into the funnel. Strong, violent tornadoes can pick up houses, animals, trees, and soil. The objects swirl around but eventually crash back to Earth. Tornadoes have even been known to pull up entire ponds and then rain fish from the sky! Because they can carry objects for several miles, tornadoes can move species to new areas.
2. Key Concept Check What are some effects of tornadoes?
Tornado Strength
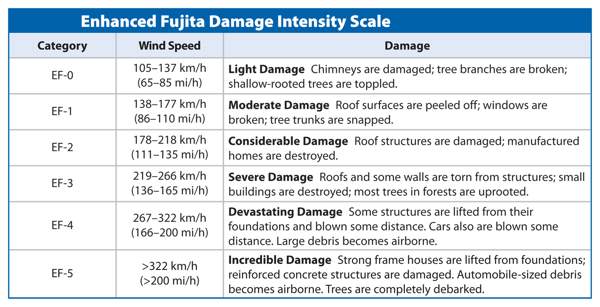
Using a scale called the Enhanced Fujita Damage Intensity Scale, shown in Table 1, meteorologists classify tornadoes by wind speed and the damage they cause. Most tornadoes are considered weak, with winds up to 177 km/h. Weak tornadoes cause damage, but not destruction. Strong tornadoes have wind speeds of 178 km/h or higher. The most violent tornadoes have wind speeds over 322 km/h and cause total destruction where they touch down. These tornadoes are rare.
Table 1 Tornadoes are described and categorized according to the damage they cause.
 Visual Check What rating would be given for a tornado that destroyed small buildings?
Visual Check What rating would be given for a tornado that destroyed small buildings?
Tornado Safety
Tornadoes can be dangerous. To help keep people safe, forecasters issue a tornado watch when the correct conditions are present to develop a tornado. If a tornado is spotted, forecasters issue a tornado warning. If a tornado warning is issued for your area, go inside a sturdy building. If possible, go to the basement. If an underground shelter is not available, move to an interior room or hallway on the lowest floor and get under a sturdy piece of furniture.
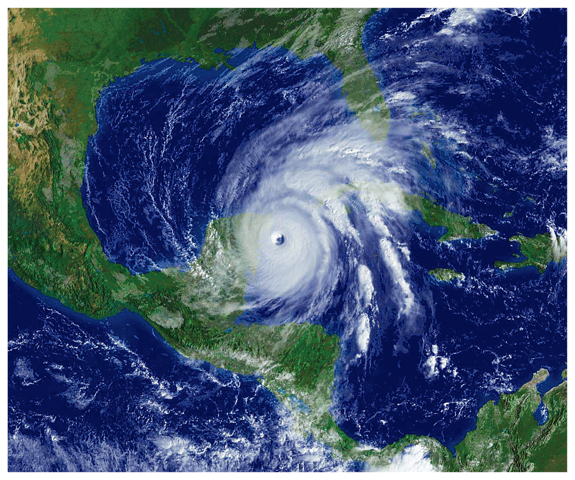
A hurricane is an intense tropical storm with winds exceeding 119 km/h. A hurricane can produce strong winds, heavy downpours, lightning, and even tornadoes. As Figure 5 shows, hurricanes are huge, averaging 480 km across. In other parts of the world, these large storms are called typhoons or tropical cyclones. When they occur in the north Atlantic Ocean, they are called hurricanes. An average of six hurricanes form each year in the north Atlantic Ocean.
At the center of these storms is a small area called the eye. In the eye, skies are clear and winds are light. Winds are strongest and the rain is most intense in the area around the eye.
A hurricane’s winds can stir up huge waves. Also, as a hurricane approaches land, its winds can push ocean water higher along the coast, creating storm surge. As shown in Figure 6, storm surge can increase the sea level 6–10 m. This is high enough to cover buildings in low coastal areas.
Figure 5 This satellite image shows a hurricane’s bands of clouds rotating counterclockwise.
 Visual Check Where is the eye of this hurricane?
Visual Check Where is the eye of this hurricane?
Figure 6 Hurricane winds can push ocean water onto land, causing storm-surge flooding. This photograph shows stormsurge flooding caused by Hurricane Ike.
Hurricane Formation
In the Atlantic Ocean, hurricane season is from June 1 to November 30. Hurricanes usually start as thunderstorms near the west coast of northern Africa. Warm ocean water provides energy for thunderstorms to become tropical storms. Humid air adds water to the growing clouds. If enough water and energy are added, tropical storms strengthen and become hurricanes. The storms move west across the Atlantic Ocean and then north along the eastern U.S. coast or into the Caribbean Sea or the Gulf of Mexico.
1. Key Concept Check How do hurricanes form?
Hurricane Impacts
Wind, waves, rain, storm surge, and tornadoes caused by a hurricane impact coastal areas when a storm comes ashore. Waves and storm surge can move sand, flood coastal towns and ecosystems, and damage buildings. Winds destroy trees, topple power lines, and blow roofs off buildings. Farther inland, rain can cause mudslides and landslides in hilly areas.
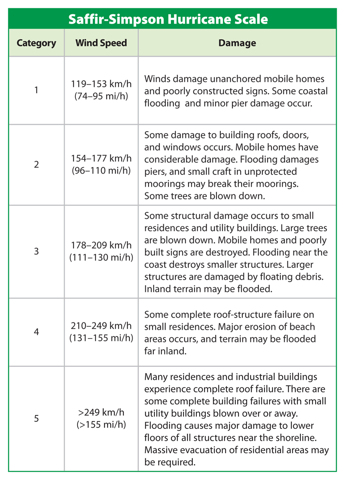
The extent of a hurricane’s damage depends on the strength of the hurricane and the characteristics of the coastal area. The strength of hurricanes is rated on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale, shown in Table 2. The scale is based on wind strength and damage caused by hurricanes.
2. Key Concept Check What are some effects of hurricanes?
Forecasting Hurricanes Scientists monitor hurricanes with satellites, ships, and buoys at sea. Sometimes crews fly airplanes into hurricanes to collect data. Radar is used when a storm is close to land. Data about the storm are put into computer models to help scientists predict the storm’s path and how large it will become.
Safety Forecasters warn people when a hurricane is on the way. They issue a hurricane warning for coastal areas that are in the predicted path of the storm. People living in those coastal areas evacuate to safer areas.
Table 2 The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale is used to measure the strength of hurricanes.
Some dramatic atmospheric events, such as winter storms, happen in just one day. Others, such as heat waves, happen over several days or weeks. Droughts can last months or years.
Winter Storms
Snowstorms can be relatively mild, such as the one shown in Figure 7, or they can be extremely hazardous. Slippery roads and reduced visibility are especially dangerous for drivers. Snow accompanied by strong winds can create blizzards. Blizzards are hazardous because temperatures are extremely low and blowing snow can reduce visibility to zero.
When conditions create freezing rain, it coats everything with a layer of ice. The weight of the ice can break tree branches and snap power lines.
Figure 7 Some natural events such as winter storms (left), extreme heat (center), and drought (right) can affect people, property, and crops.
Extreme Heat
Unusually hot weather that lasts for several days is called a heat wave. Heat waves are more common in large cities, where buildings and pavement, such as the roadway pictured in Figure 7, absorb and hold the Sun’s thermal energy. Heat waves can lead to heat stroke and heat exhaustion for some people. Both conditions can be life-threatening.
Drought
A drought is a period of below average precipitation in an area that can last for several months or years. Changing atmospheric patterns can cause drought. For example, changing wind patterns can block fronts from reaching an area. This can prevent rain from falling. Less water changes rivers and other ecosystems. There might not be enough water for crops. As shown in Figure 7, if plants die for lack of water, winds can remove the top layer of fertile soil.
1. Key Concept Check What are some effects of winter storms, extreme heat, and drought?
Lesson Review
Visual Summary
The largest thunderstorms form where a warm, moist air mass meets a cool, dry air mass. Thunderstorms produce heavy rains, lightning, thunder, and sometimes tornadoes.
Hurricanes are some of the largest and most powerful weather events. In the Pacific Ocean, hurricanes are called typhoons.
Severe weather such as tornadoes and winter storms are hazardous natural events that impact people and the environment.
What do you think NOW?
You first read the statements below at the beginning of the lesson.
1. Thunder produces lightning.
2. In some parts of the world, hurricanes are called typhoons.
Did you change your mind about whether you agree or disagree with the statements? Rewrite any false statements to make them true.
Use Vocabulary
1. Sea level can be raised 6-10 m by __________.
2. Thunderstorms occur in __________ clouds.
3. Define drought in your own words.
Understand Key Concepts
4. Atlantic hurricanes form
A.in Tornado Alley.
B.over south Florida.
C.near Bermuda’s high-pressure system.
D.off the west coast of northern Africa.
5. Compare the impacts of thunderstorms, tornadoes, and hurricanes.
6. Which is the best thing to do when a tornado warning is issued?
A.Go inside a small building without a foundation.
B.Go outside and look for the tornado.
C.Go to a basement or interior room.
D.Go to a high point, such as a hill.
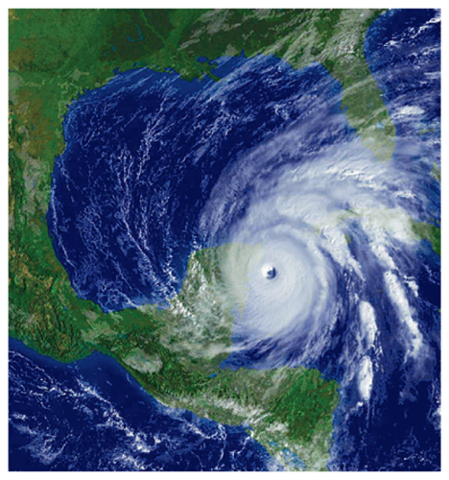
7. What will happen to the hurricane shown below as it approaches the United States?
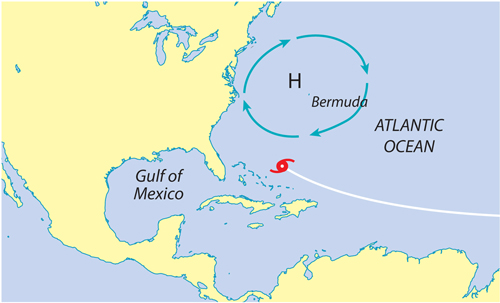

A.The storm will decrease in size.
B.The storm will increase in size.
C.The storm will move along the East Coast.
D.The storm will move into the Gulf of Mexico.
Interpret Graphics
8. Analyze Where in this illustration below would the positive and negative charges build up that could cause a cloud-to-ground lightning strike?


9. Sequence Copy the graphic organizer below. List the steps a storm goes through to become a hurricane, starting with a thunderstorm.
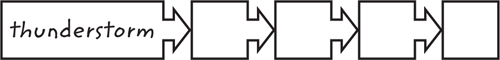

Critical Thinking
10. Explain Why do so many tornadoes occur in Tornado Alley?
11. Analyze How is drought different from other weather events described in this lesson?
12. Hypothesize If temperatures in the Gulf of Mexico were higher than in the Atlantic Ocean, how might this affect a hurricane as it moves into the Gulf of Mexico?
13. Predict how catastrophic events can impact ecosystems.
14. How does weather impact the environment?


Warren Faidley/Photolibrary
Writing in Science
15. Instruct Write a safety brochure giving instructions on how to recognize severe weather and how to stay safe.
Math Skills
Using Geometry
16. The eye of a hurricane has a radius of 50 km.
What is the area of the eye?
What is the area of the eye?
17.What is the circumference of the eye?
The area covered by the destructive winds in a particular hurricane has a diameter of 120 km.
18. What area do the destructive winds cover?
[Hint: radius is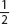 diameter.]
diameter.]
[Hint: radius is
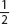 diameter.]
diameter.]
19. What is the circumference of the hurricane?
20. A hurricane has a cirumference of 1,000 km. What is the radius of the hurricane?
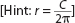
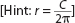







0 comments:
Post a Comment